Introduction
The Multi Request credential allows you to make multiple HTTP requests to fetch an access token or API key, every time the credential is used. For instance, you could use this to fetch runtime credentials from a service like Vault or CyberArk Secrets Hub.
When used in a HTTP request action, this means that three web requests will be made for each run: two to fetch the credential value, and a third to run the action itself.
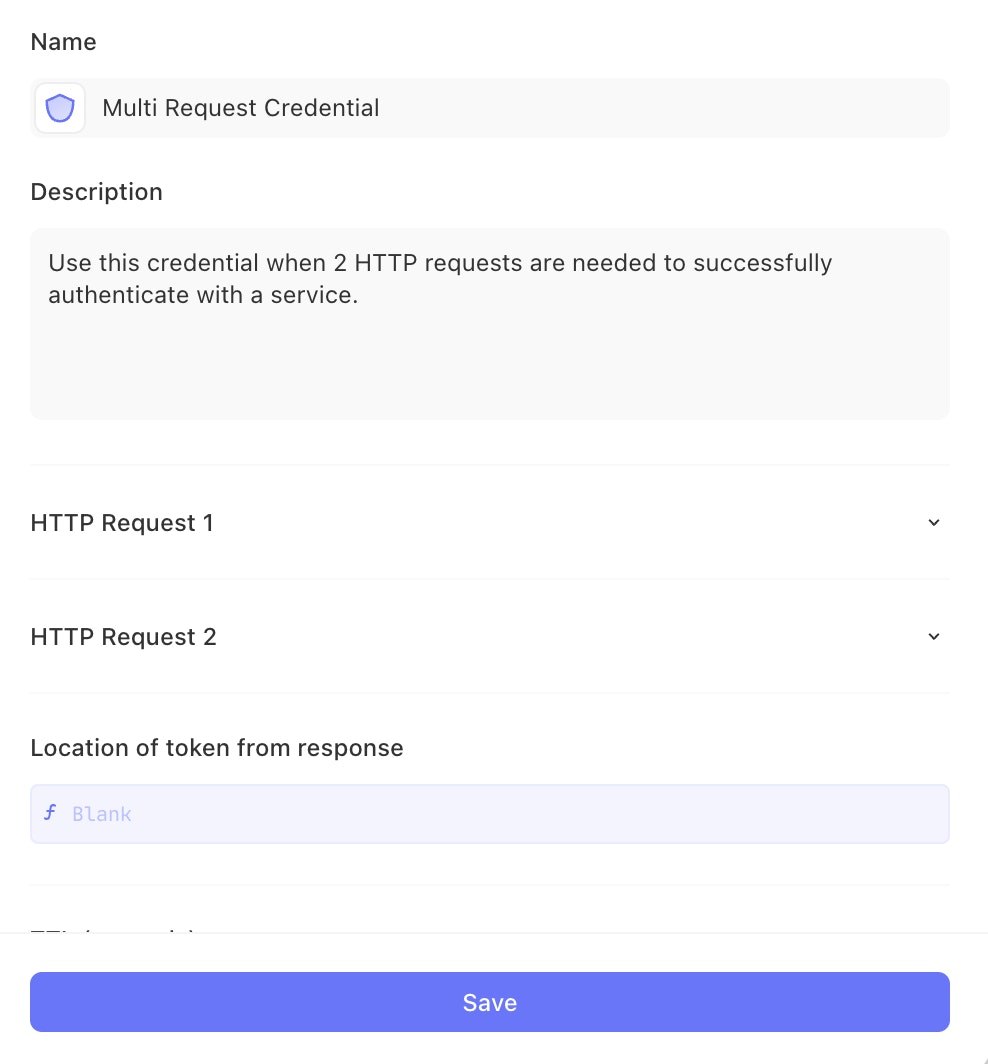
Configuring the credential
This is our most complex credential type, and there are a few steps involved.
First, configure HTTP Request 1
You’ll need to enter the URL, content type, method, and payload for the request you want to make to fetch your credential value. Beyond these basics, you can add any other request option that our HTTP request action supports.
🪄Tip

Additionally, you can input a secret value for use in the request. This is securely stored, and can be referred to in formulas within the request fields (params, headers, etc) as secret.
Next, run a test request
Once your request is configured, press ‘Run request’ to run a test request. The result of the request will be displayed. Tweak and re-run tests until the result is as expected.
Then, configure HTTP Request 2
This is the second step needed to get the secret value that will be used in outbound calls to your service. Configure it similarly to how you configured the first request and run a test request.
Referencing HTTP Request 1:
The output of HTTP request 1 will be needed in HTTP Request 2. To reference the output of the first request, use the key PREVIOUS_STEP and specify the path to the token or specified item needed to successfully make the second request.
Finally, configure the location of token
Use the formula builder in the ‘Location of token from response’ field to describe the path to the token value in your test request’s response. This will only reference the output of HTTP Request 2.
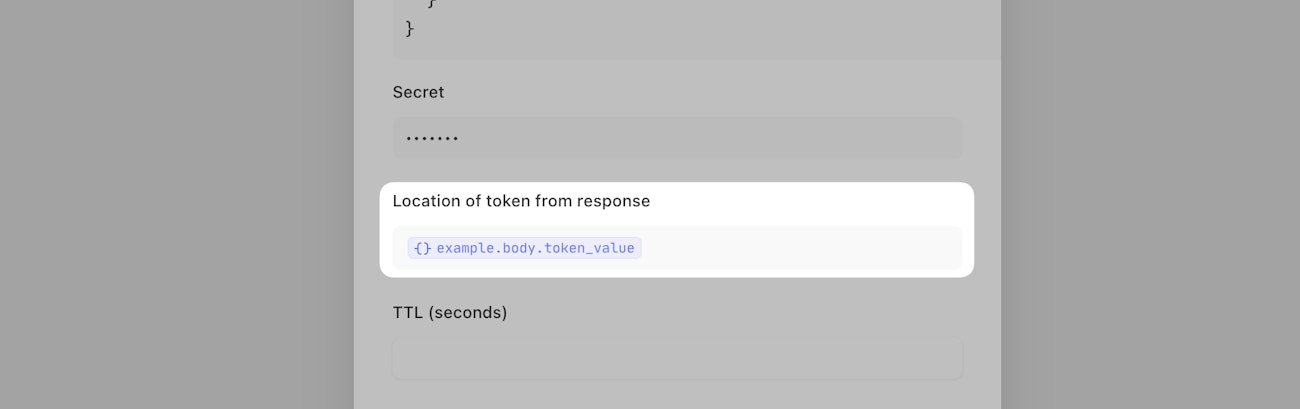
That’s it! The token will be obtained from this location of the response every time the credential is used, and its request fires.