The AI agent action allows you to securely and privately run a large language model (LLM) at any point in your workflow. It supports two modes of operation: task and chat, enabling both behind-the-scenes automation and interactive user experiences.
AI agent action usage is based on a credits system: all tenants include a monthly credit allowance, and each execution of the action deducts credits. See more details on credits and executions.
Learn more about how AI works in Tines at Tines Explained.
Features
Invoke an LLM on demand in your workflow
AI models run inside Tines's infrastructure, with strong security and privacy guarantees.
Choose from a variety of language models
Please note that the list of available models may vary depending on your tenant’s region.
Support for the AI agent action to use tools
Support for the AI to write and run code to analyse data
Configure system-level instructions to guide the AI’s behavior
Include image data to take advantage of Claude's vision capabilities
Host a user-facing AI chat experience (Chat mode)
Configure alerts for when the action's token usage exceeds a certain threshold
Modes
Task Mode
Task mode supports invoking a large language model either in a simple one-shot fashion (prompt → response) or as an autonomous agent that can use tools to complete tasks.
When tools are attached, the model engages in a self-directed reasoning loop, invoking tools as needed until a solution is reached.
Chat Mode
Chat mode enables a conversational experience hosted on a Tines page.
End-users can interact with the AI agent action in real time. The chat continues until the AI achieves a defined objective specified in the system instructions, at which point the action completes and emits a final event.
Creating a well defined, clear goal for the AI agent to work towards will help it to understand when the chat should be ended.
You can also add an explicit line to your system instructions that tells the AI agent when the chat should be considered complete. For example:
"The goal is to make suggestions for how to improve someone's Jira issue write up. Once suggestions have been successfully shared or determined unnecessary, end the conversation."
Or:
"Your goal is to assist a user in resetting their device logins. Once you've reset the user's account, end the conversation."
File attachments
AI Agent chat mode pages allow users to attach the following file types:
Images:
PNG,JPEG,GIF,WEBPDocuments:
PDF,CSV,MD,TXT,DOC,DOCX,XLS,XLSX
Attachment limits:
Users can attach up to three files per message.
Each attachment may be up to 4.5MB in size.
If you're using a provider other than the default Tines provider, supported file types may vary.
Tools
Tools are functions the model can access to perform specialized tasks beyond its built-in capabilities.
There are four categories of tools you can attach to the AI agent action, supported in both task and chat mode.
Templates
Tines provides pre-built public templates for popular products to save you time building out workflows.
These templates can be added and configured as tools for the AI agent action.
Additionally, you can add private, user-defined templates as tools.
See our templates documentation for more information.
Send to Story
You can attach existing Tines Stories as tools using Send to Story, which lets the AI agent action pass data into another Story as input.
Note that these external Stories exist within a separate change control scope from the Story containing the AI agent action.
See our Send to Story documentation for more information.
Timeout settings
You can configure timeouts for Send-to-Story tools by adding the Timeout Duration option to the tool. With this option set, the agent will gracefully conclude the tool use if the underlying story did not complete in time. This option will override whatever timeout duration is set in the Send-to-Story settings.
Custom tools
Custom tools allow builders to define and configure tools directly within the same Story as the AI agent action, keeping everything under a single change control scope.
This facilitates tasks that may not be covered by existing public templates or tasks that require multi-action workflows that reference dynamic input values.
Internal tools
AI agents have built-in functionalities designed to enhance and extend the capabilities of an agent without additional configuration.
Think
A scratchpad that an agent can use to plan out its actions before taking them. Designed based on Anthropic's research.
Code Analysis
An ability to write and run code, allowing the agent to perform data analysis and generate charts
MCP
Tines supports connecting to remote MCP (Model Context Protocol) servers, allowing the AI Agent action to call tools exposed by those servers. This enables integration with external systems and services that implement the MCP specification.
Supported transports
We currently support the following MCP transports:
Streamable HTTP
Plain HTTP
Note: SSE and stdio transports are not supported at this time.
Supported authentication methods
Bearer and generic header authentication
Note: OAuth is not supported at this time.
Supported features
When connecting to MCP servers, only Tools are supported.
We do not support:
Resources
Prompts
Notifications
Using MCP tools
Once connected to a remote MCP server, any tools it exposes will appear alongside your other configured tools in the AI agent action. These tools can then be invoked by the agent in the same way as Send to Story, Template, or Custom tools.
Configuration options
System instructions:Optional system-level instructions that define the rules, context, and constraints for the AI. In Chat mode, this should define the bot’s goal; the chat ends when the goal is achieved.Tools: A list of tools the AI agent action can use. When provided, the AI acts autonomously to decide if/when to use each tool.Output schema: A JSON schema to validate the output structure.Model: The LLM to use (default: the default smart model).
Task mode options
Prompt: The input to send to the model. Can include input data, examples, or instructions.Image: (Claude models only) Base64-encoded image content, or an array of images.Temperature: Controls the creativity of the output. Range: 0–1 (default: 0.2).Timeout: Timeout for the LLM request in seconds (default: 30).Retries: Max number of retries (default: 25).
Chat mode options
URL identifier: Defines the public URL for the chat page.Access control: Configuration for who can access the chat.Theming options: Customize the chat page’s appearance:
Action color: Primary UI colorPage logo: Image to displayAppearance: "light" or "dark" mode
Initial message: Message displayed to the user when the chat starts.Idle timeout (minutes): Automatically end the chat after a certain number of minutes without user activity.Idle timeout only applies to chats where the user has sent at least one message.
The timer resets whenever the user begins typing a message. A warning is displayed when fewer than 30 seconds remain before the chat ends automatically.
When a chat times out, the
outcomefield undermetain the event output will beidle_timeout. This allows you to handle timeouts in your story run.
Limits
Emitted event
When in task mode with no tools attached, a single event is emitted each time the action runs. This event contains output from the AI model.
{
"output": "Estimated severity: high"
}If the model returns valid JSON, or you have an output schema configured, Tines will automatically parse this in the event data:
{
"output": {
"estimated_severity": "high"
}
}When using chat or task mode with tools, the event payload will also include the full conversation steps. For example:
{
"steps": [
{
"role": "user",
"text": "How many users are on this tenant?"
},
{
"role": "agent",
"text": "I'll help you find out how many users are on this tenant by retrieving the user list"
},
{
"role": "tool",
"tool_name": "think",
"inputs": {
"input": "The user wants to know the total number of users on this tenant. I should use the list_users function to get this information."
},
"output": "Thought logged"
}
]
}Tines will include a metadata field in the event payload that specifies the model used, input and output token counts, credits consumed, duration elapsed in seconds, and remaining credits.
{
"input_tokens": 1943,
"output_tokens": 417,
"credits_used": 3,
"remaining_credits": 4759,
"model": "eu.anthropic.claude-3-7-sonnet-20250219-v1:0",
"duration": 266.20275563
}Example configuration options
Proposing remediation steps for a security alert (alert_data):
{
"prompt": "Summarize the potential remediation steps for the alert\n\n Data:<<alert_data>>"
}Analyzing a support request from a user (support_request):
{
"prompt": "Help the user with their product issue.\n\n Data:<<support_request.query>>",
"image": "=support_request.screenshot.contents"
}A security remediation agent.
{
"mode": "task",
"prompt": "Remediate the following alert based on the step defined below:\n\n<alert>\n```\n<<cases_action.body.case>>\n```\n</alert>\n\n<remediation_task>\n<<cases_action.body.button.label>>\n</remediation_task>",
"instructions": "You are a Security Remediation Agent responsible for executing remediation actions for security alerts.\n\nYour primary responsibilities are:\n\n1. Carefully analyze the remediation instructions provided in security alerts\n2. Execute the specified remediation actions using the appropriate tools available to you\n3. Report back on the outcome of each remediation action to the originating case using a Case Note\n4. Delete the \"Case Action\" that triggered the alert. This can be found by its ID.\n\nWhen receiving remediation instructions:\n- Parse the instruction carefully (e.g., \"Block URL xyz\", \"Disable user account abc\")\n- Identify the specific action required and the target of that action\n- Select the appropriate tool to execute the requested action\n- Execute the action precisely as instructed\n- Document all steps taken during remediation\n- Report success or failure of the remediation action\n- Include any relevant details or errors encountered during remediation\n\nAvailable remediation actions may include:\n- Blocking URLs/domains\n- Disabling user accounts\n- Revoking access tokens\n- Isolating endpoints\n- Adding IPs to blocklists\n- Removing malicious files\n- Resetting credentials\n\nAfter completing the remediation action, always:\n1. Verify the action was successful\n2. Create a detailed Case Note on the originating case with:\n - The action that was taken\n - The outcome (success/failure)\n - Any relevant details or metrics\n - Timestamp of when the action was completed\n - Any recommended follow-up actions\n3. Delete the \"Case Action\" that triggered the alert. This can be found by its ID.\n\nNever deviate from the explicit remediation instructions provided. If instructions are unclear or appear potentially harmful, request clarification before proceeding.\n\nUse the following example for formatting:\n```\n## Remediation Action Completed: Block Sender Domain\n\nCompleted the remediation action to block the sender domain **suspicious.ru**.\n\n### Actions Taken:\n1. ✅ Successfully added the domain to the Sublime Security suspicious email addresses list\n2. ❌ Attempted to add the domain to CrowdStrike IOC blocklist but received an error: \"No IOCs could be identified\"\n\n### Recommendation:\nConsider manually adding this domain to your email gateway blocklist to ensure complete protection.\n\n"
}Chat mode
A support assistant that assists users troubleshoot IT issues.
{
"mode": "chat",
"instructions": "You are a helpful assistant that helps users troubleshoot IT issues.",
"initial_message": "Hi, how can I help you today?",
"visibility": "tenant",
"pages_appearance_mode": "light",
"pages_action_color": "#777FFF",
"page_mode": "success_page",
"page_logo": null,
"url_identifier": "6922c10ca8fe089ad0706eb31cb3a4de",
"idle_timeout_minutes": 15
}Monitoring Alerts
You can configure two types of usage alerts from the AI Agent action's status panel:
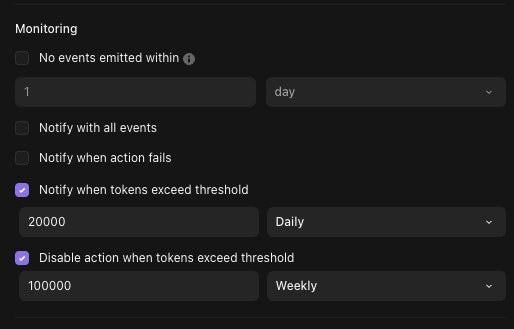
Token usage thresholds can be configured for a particular period
Notify: When the AI agent uses enough tokens to exceed the threshold for the selected period (Daily, Weekly, Monthly, All time), the recipients of the story will be notified.
Disable action: Will notify the recipients of the story when the threshold is exceeded, but will also disable the action to prevent further token usage.
Slack App Configuration
To configure a Slack app for your AI Agent action, go to the "Slack app" section of your agent's build panel and click "connect", then follow the on-screen instructions to create a new Slack app in your workspace and connect it to your agent. Note that only AI Agent actions in chat mode can be connected to Slack.
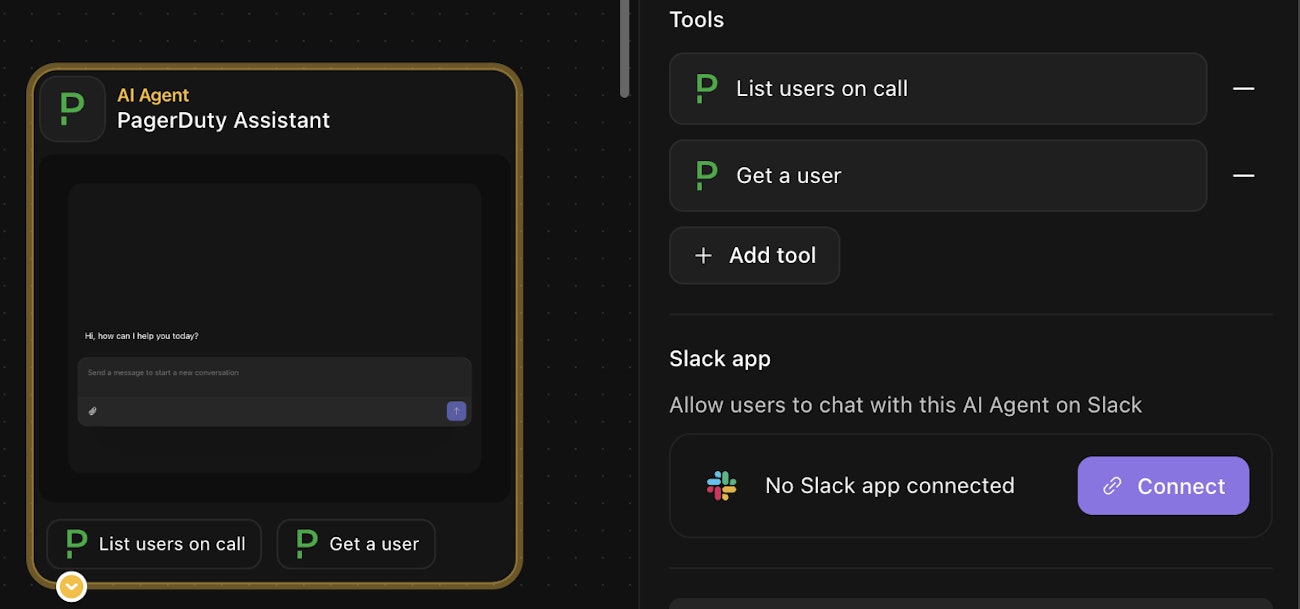
Once connected, you can test the connection by initiating a conversation with the agent in Slack (see this article from Slack on the different ways to interact with agents in your workspace).
If you are connecting an agent as part of a new change control draft, you will need to perform an extra step if you wish to test the connection before setting it live. Within the "Event Subscriptions" section of your Slack app's settings, you will need to append ?draft=DRAFT_NAME to the Request URL.
Once your draft has been merged into the live story, you should return to this setting's page and remove the ?draft=DRAFT_NAME part from the Request URL.
Please note: to avoid depleting your tenant-wide credits, the AI Agent action type is not available in your personal teams.